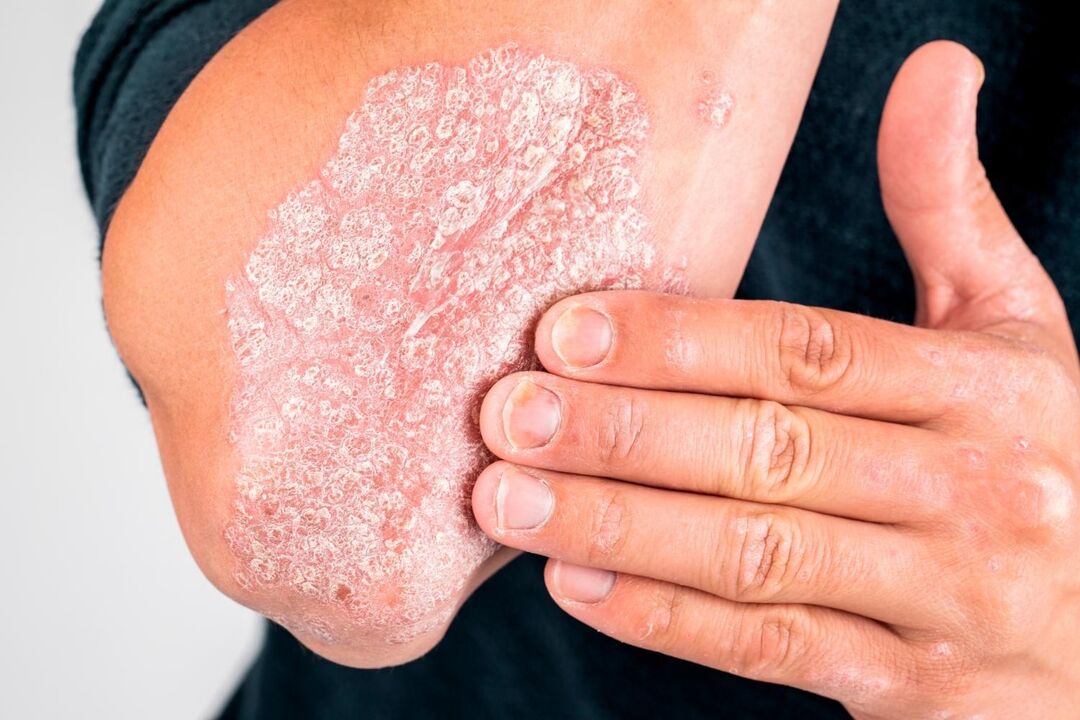
A pathological condition characterized by scaly and nodular changes on the skin and nails is called psoriasis. Dermatologists are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
Psoriasis is a chronic skin and nail disease in which a rash of pink nodules and silvery scales appear on the skin. Usually nodules merge into large plaques, where the skin is quickly covered with scales. With prolonged development of the disease, joint damage is possible, accompanied by impaired movement and constant pain. Different forms of psoriasis differ in the degree of skin damage: patients may have only fine spots on the scalp or large plaques on different parts of the body. The possibility of experiencing psoriasis complications also depends on many factors. This disease is very dangerous for pregnant women, because the pustular form of this disease can cause miscarriage.
About the disease
Psoriasis is one of the most common skin diseases. The first symptoms of skin changes usually occur between the ages of 18 and 35. Often psoriasis occurs against the background of cardiovascular disorders, Crohn's disease and depression. About 30% of patients experience joint damage (arthritis). It is impossible to eliminate the cause of psoriasis, however, symptomatic therapy can significantly reduce the course of the disease.
Types of psoriasis
Depending on the symptoms that occur, several types of psoriasis are distinguished:
- plaque: characterized by the appearance of a classic plaque covered with silvery scales; preferred location: elbows, knees, torso, scalp;
- teardrop-shaped: the main manifestation is an orange-pink nodule with a size between 1 and 10 mm;
- nail psoriasis: the nail plate is mostly affected;
- large fold psoriasis: rashes occur in the armpits, in the folds of the neck, on the genitals and other places with excessive friction; this form is more common in obese people;
- scalp psoriasis: affected scalp;
- arthropathic psoriasis (psoriatic arthritis): affected joints;
- pustular psoriasis: several small vesicles with pus appear on the patient's skin;
- psoriatic erythroderma: in addition to the rash, there is significant reddening of the skin in the area of the rash.
Symptoms of psoriasis
Most often, plaques appear on the forearms, lower legs, navel and scalp. The pustular form of psoriasis is characterized by the formation of pus-filled blisters on the skin. At a certain period, many patients experience changes in the color and structure of the nails. Damage to the skin scales leads to the appearance of accurate bleeding. The patient also complains of itchy skin. Skin changes periodically disappear and reappear.
Other symptoms and signs:
- the appearance of red spots in the area of skin folds;
- profuse rash occurs after infectious diseases and stress;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- the appearance of new skin rashes in the winter months;
- joint pain;
- impaired mobility in the affected joint area;
- dryness and skin hypersensitivity.
Plaque absorption usually starts from the center, as a result of which psoriatic elements acquire an annular or garland-like shape. Temporary depigmentation (pseudo leukoderma) remains at the site of the resolved rash. During the period of incomplete remission, individual "task" plaques may remain in certain areas of the skin (more often in the areas of the elbow and knee joints).
The most severe types of psoriasis are psoriatic erythroderma and arthropathic psoriasis.
In psoriatic erythroderma, the entire (or almost all) skin is involved in the pathological process. The skin becomes tense, rough, infiltrated, red, with numerous large and small lamellar peeling on the surface. Peripheral lymph nodes increase, subfebrile temperature appears, the general condition of the patient is disturbed, changes in blood (leukocytosis, increased ESR), urine (proteinuria) are observed. The development of erythroderma is promoted by irrational and irritating therapy in the progressive stage of psoriasis.
Arthropathic psoriasis is characterized by lesions mainly on the small joints of the hands and feet, less often on the wrists, ankles, intervertebral, etc. , accompanied by severe pain and swelling of the joints, limitation of movement and their deformity. X-ray revealed lysis of the distal phalanges of the fingers and changes in the joint, similar to rheumatoid arthritis. Waaler-Rose test and latex test are usually negative. In the blood, leukocytosis, increased ESR, hypergammaglobulinemia. Articular involvement may be associated with skin lesions or be isolated for several years.
With all these forms of psoriasis, it is possible to damage the nail in the form of a pierced nail plate ("thimbal phenomenon"), its clouding or thickening up to onychogryphosis. The course of this disease is chronic and undulating. The seasonality of the process is usually expressed - a decline in winter with a significant increase in summer (winter type), less often - the opposite (summer type).
Causes of psoriasis
The exact mechanism of psoriasis formation is still not understood. It is considered an autoimmune disease in which the body's defense system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. T cells and neutrophils needed to fight pathogens can begin to attack skin cells and joint structures. In this case, characteristic changes in the skin occur, including the formation of bubbles with inflammatory fluid. The expansion of blood vessels in the area of inflammation is accompanied by redness of the skin. Autoimmune diseases can be caused by hereditary factors.
Additional risk factors:
- skin infection. First of all, this is a bacterial infection caused by streptococcus;
- skin damage due to wounds and burns;
- prolonged stress and psychotraumatic factors;
- alcohol and smoking;
- lack of vitamin D in the body;
- taking certain medications, including lithium and beta blockers;
- unfavorable family history. The discovery of psoriasis in a close relative of the patient indicates a possible genetic predisposition to the disease;
- acquired or congenital immunodeficiency. It may be HIV infection, AIDS, or other conditions.
Despite the discovery of the purported immunopathological cause of psoriasis, the disease is still poorly understood. There are a large number of diseases and lifestyle characteristics that trigger the manifestation of hidden factors of predisposition to this disease.
Diagnosis of psoriasis
If skin changes appear, you should consult a dermatologist. Our clinic doctor first conducts a general examination of the skin to assess the nature of the rash. Gentle scraping allows you to detect exfoliating papules and thin films under the nodules. Under the film, a moist surface of the skin is found, prone to small bleeding. At the same time, there are atypical signs of psoriasis that resemble other diseases, so doctors need to carry out instrumental and laboratory diagnostics.
- Blood analysis. Dermatologists prescribe venous blood tests to rule out other diseases and detect signs of psoriasis. In the treatment room, the nurse treats the skin of the patient's cubital fossa with an antiseptic, uses a tourniquet, and takes blood with a syringe. In our laboratory, specialists first exclude the presence of rheumatoid factors. In pustular psoriasis, an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is often found. High levels of uric acid are detected;
- Examination of pustular fluid. The doctor collects the fluid in a sterile container and sends the material to the laboratory. Microbiological examination did not reveal a bacterial culture, but an increase in the number of neutrophils characteristic of psoriasis was found;
- Skin biopsy. Dermatologists prescribe this study to make an accurate diagnosis for atypical rashes. During the procedure, the doctor treats the skin with an antiseptic, anesthetizes and removes a small area of skin with a scalpel. Tissue material is studied in our clinic laboratory using a microscope. The results allow to clarify the cellular composition of the nodule;
- X-ray of the affected joint. Doctors prescribe this study to determine the type of arthritis. Also, in severe complications of arthropathic psoriasis, bone X-ray diagnostics are required;
- Scrape the skin to get rid of the fungus. The doctor cleans the surface of the skin and, using a special spatula, collects some scales for microbiological examination. This analysis is especially necessary if the rash occurs only in the area of the feet and nails.
If necessary, a consultation with a rheumatologist is carried out.
Expert opinion
Psoriasis is a disease with many manifestations. It can be almost invisible or cause serious health problems. The most dangerous complication of psoriasis is joint damage, which can cause disability in patients. Also, this disease can lead to autoimmune disorders, in particular, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, metabolic pathology, erectile dysfunction in men. Women with psoriasis may experience infertility and miscarriage. To avoid these complications, it is necessary to consult a doctor immediately after the appearance of suspicious signs, and with a diagnosed diagnosis, carefully follow all the recommendations of specialists.
Treatment of psoriasis
The main goal of psoriasis treatment is symptomatic therapy. Patients need drugs that reduce inflammation and prevent the formation of skin rashes. In addition to drug therapy, the dermatologist of our clinic necessarily prescribes a special diet for the patient. Normalizing lifestyle and eliminating stress factors can reduce the severity of psoriasis symptoms.
Depending on the condition, dermatologists may use different methods to treat the disease.
- Administration of corticosteroids. Dermatologists prescribe ointments containing these drugs. Beneficial effects of corticosteroids include reducing inflammation in tissues and eliminating itching;
- Vitamin D supplements. The synthetic form of this vitamin slows down the growth of skin cells, thereby preventing the formation of scales and nodules;
- Therapy with drugs containing derivatives of vitamin A. Dermatologists prescribe ointments based on retinoids to reduce inflammation and itching. These drugs increase the skin's sensitivity to light, so sunscreen must be used;
- Use of calcineurin inhibitors. These are immunosuppressants that reduce inflammation. Dermatologists prescribe topical agents such as tacrolimus. The drugs are used in short courses to prevent the development of side effects and complications;
- Skin treatment with salicylic acid to remove dead cells. Dermatologists prescribe this drug along with corticosteroids for complex skin treatment;
- Use a moisturizer to get rid of dry and itchy skin;
- Irradiation of the skin with ultraviolet light. This safe physiotherapeutic treatment method improves local immune function. The doctor selects an individual radiation dose for the patient;
- Phototherapy. This method involves irradiating the skin using a special device. Phototherapy combines the technology of laser therapy and photochemotherapy;
- Joint puncture in severe psoriasis. The doctor treats the skin at the puncture site with an antiseptic, anesthetizes the tissue and inserts a needle. With the help of a syringe, drugs are injected into the joint cavity to reduce the inflammatory process.
Dermatologists control all stages of treatment to achieve the best results and prevent complications. Corticosteroids, retinoids and calcineurin inhibitors are used strictly under expert supervision.
Prevention of psoriasis
The recommendations of our clinic's dermatologists will help reduce the severity of skin rashes and ease the course of the disease.
Prevention of psoriasis exacerbations:
- reduce anxiety and stress by improving sleep, avoiding coffee, and taking prescription tranquilizers;
- exclusion from the diet of foods containing allergens;
- timely treatment of infectious skin diseases.
Restoration
Psoriasis is a chronic disease that cannot be cured. Remedial measures are aimed at preventing recurrence. Depending on the form of the disease, physiotherapy, spa treatment, mud therapy, therapeutic baths and other procedures may be prescribed.
Question and answer
Is it possible to treat psoriasis with folk remedies?
There is no method that has been proven to be effective. It is important not to believe in dubious types of treatment, but to follow the recommendations of the attending physician.
Does stress affect the course of psoriasis?
Yes, stressful situations can worsen the course of the disease.























